In addition, many companies will state that they use the “lower of cost or market” when valuing inventory. Another inventory cost accounting method that is also widely used by both public vs. private companies is the Average Cost method. The last in, first out (LIFO) accounting method assumes that the latest items bought are the first items to be sold.
Influences On Business
Another reason why businesses would use LIFO is that during periods of inflation, the LIFO method matches higher cost inventory with revenue. To use the weighted average model, one divides the cost of the goods that are available for sale by the number of those units still on the shelf. This calculation yields the weighted average cost per unit—a figure that can then be used to assign a cost to both ending inventory and the cost of goods sold. The Sterling example computes inventory valuation for a retailer, and this accounting process also applies to manufacturers and wholesalers (distributors). The costs included for manufacturers, however, are different from the costs for retailers and wholesalers. You also need to understand the regulatory and tax issues related to inventory valuation.FIFO is the more straightforward method to use, and most businesses stick with the FIFO method.
How do you calculate FIFO and LIFO?
In addition, companies often try to match the physical movement of inventory to the inventory method they use. If inflation were nonexistent, then all three of the inventory valuation methods would produce the same exact results. When prices are stable, our bakery example from earlier would be able to produce all of its bread loaves at $1, and LIFO, FIFO, and average cost would give us a cost of $1 per loaf.
- The average cost method produces results that fall somewhere between FIFO and LIFO.
- On the other hand, a company that uses the LIFO method will be reporting a lower value of net worth and hence will appear comparatively less attractive to the investors.
- This means taxable net income is lower under the LIFO method and the resulting tax liability is lower under the LIFO method.
- Under FIFO, the cost of goods sold is generally lower during periods of inflation, leading to higher taxable income.
Tax Implications
The average cost is a third accounting method that calculates inventory cost as the total cost of inventory divided by total units purchased. Most businesses use either FIFO or LIFO, and sole proprietors typically use average cost. This means that if inventory values were to plummet, their valuations would represent the market value (or replacement cost) instead of LIFO, FIFO, or average cost. Companies with perishable goods or items heavily subject to obsolescence are more likely to use LIFO. Logistically, that grocery store is more likely to try to sell slightly older bananas as opposed to the most recently delivered. Should the company sell the most recent perishable good it receives, the oldest inventory items will likely go bad.
All of that is due to the difference in the values of COGS, which in turn is due to the use of two different methods of inventory valuation. When a business uses FIFO, the oldest cost of an item in an inventory will be removed first when one of those items is sold. This oldest cost will then be reported on the income statement as part of the cost of goods sold.
Does IFRS Permit LIFO?
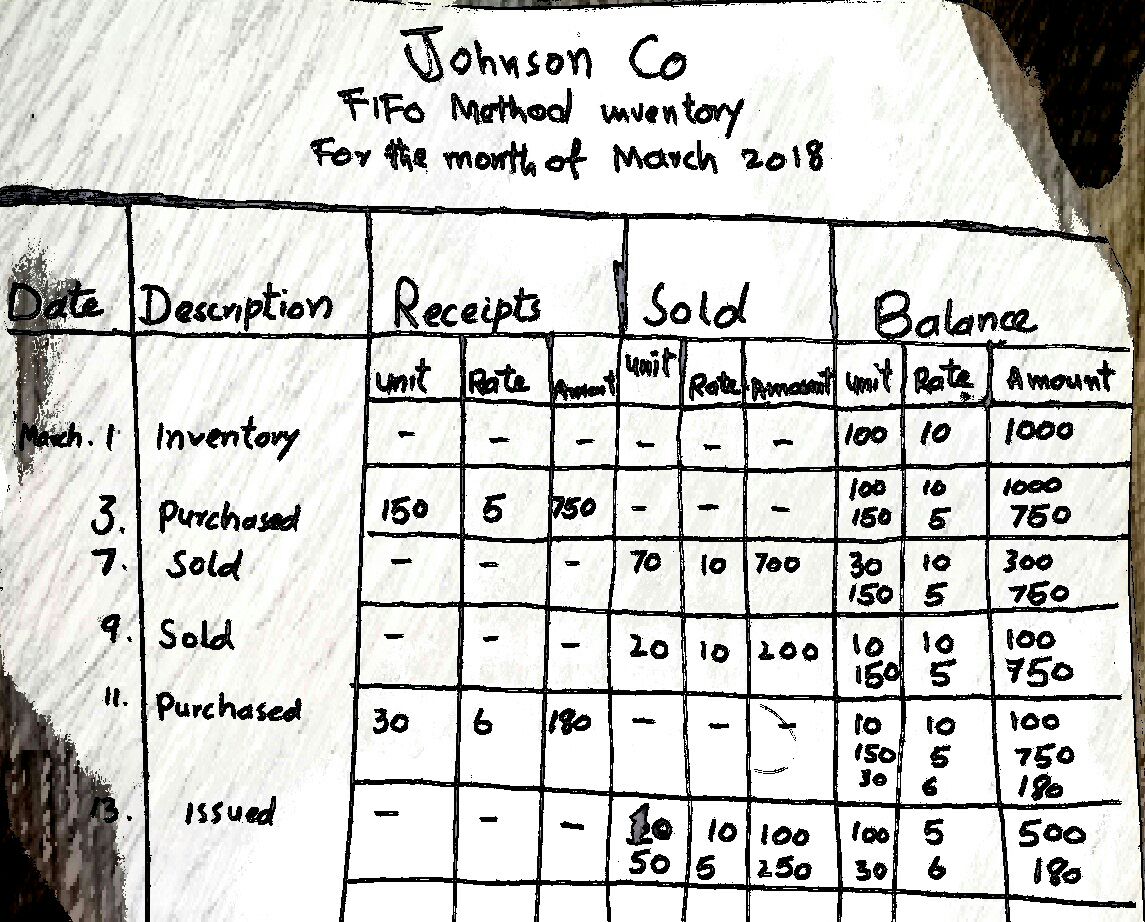
The company’s bookkeeping total inventory cost is $13,100, and the cost is allocated to either the cost of goods sold balance or ending inventory. Two hundred fifty shirts are purchased, and 120 are sold, leaving 130 units in ending inventory. Before diving into the inventory valuation methods, you first need to review the inventory formula. The components of the formula are used to calculate FIFO and LIFO accounting values. Inventory is often the most significant asset balance on the balance sheet.
FIFO and LIFO are two methods of accounting for inventory purchases, or more specifically, for estimating the value of inventory sold in a given period. Both these methods are pure methods of accounting for and reporting inventory value. Whichever method is adopted, it does not govern the addition or removal of inventory from the stock for further processing or selling. Shawn Company had 100 units in beginning inventory at a total cost of $10,000.
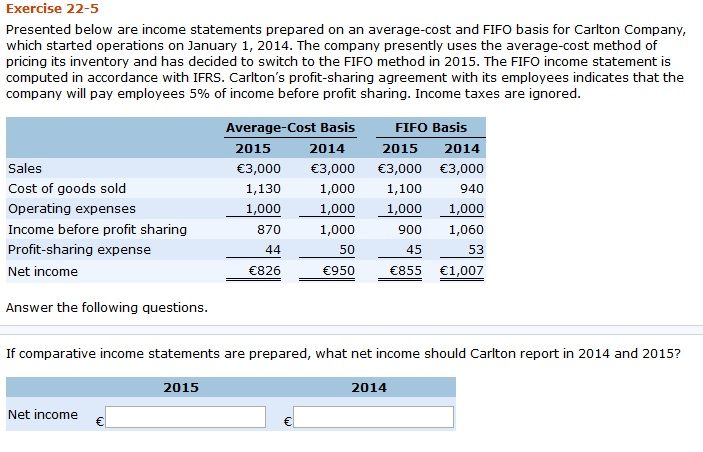
On the other hand, on the Balance Sheet, the inventory cost still in stock will equal the cost of the oldest inventory present in the stock. It, in turn, means the cost of inventory sold as reported on the profit and loss statement will be taken as that of the oldest inventory present in the stock. On the other hand, on the Balance Sheet, the cost of the inventory still in stock will be taken equal to the cost what’s your preferred federal income tax filing vendor of the latest inventory added to the stock. The management of Danica Co. asks your help in determining the comparative effects of the FIFO and LIFO inventory cost flow methods. The management of Gresa Inc. is reevaluating the appropriateness of using its present inventory cost flow method, which is average-cost. Both the LIFO and FIFO methods are permitted under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
- Pin Up Online Casino oyunu | Onlayn rulet oynayın - January 8, 2025
- Bet with Cat 💰 Offers free spin 💰 Great Customer Support. - January 7, 2025
- Jazz: O que é, significado - January 7, 2025






Leave a Reply